Approaches for Learning Happiness Development among Graduate Students in the Faculty of Education, Ramkhamhaeng University
Main Article Content
Abstract
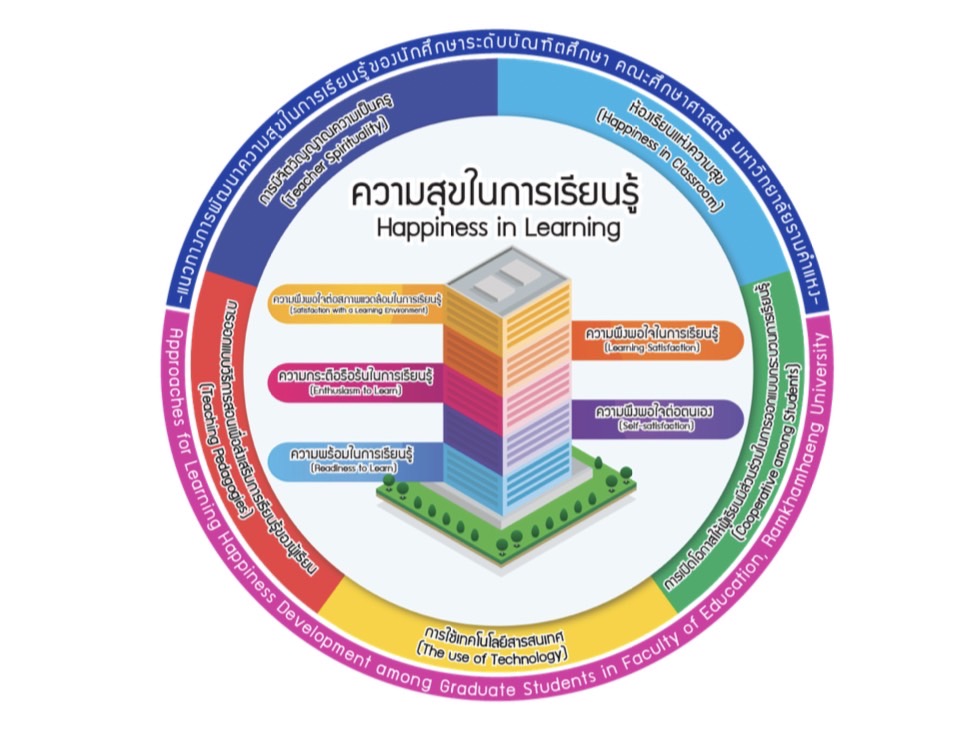
The mixed methods research was applied and divided into two phases. Phase one involved quantitative research aimed at studying the degree of success, the importance of stage, and the modified Priority Needs Index (PNImodified) of learning happiness among graduate students in the Faculty of Education, Ramkhamhaeng University (EDU-RU). The sample size of 217 graduate students in the EDU-RU. Then, multi-stage random sampling was used to select graduate students from the EDU-RU in this research. The instrument is a five-level Likert scale. In phase two, qualitative research was conducted to develop learning happiness development approaches among graduate students in the EDU-RU. Using purposive sampling, there was a total of nine participants, including five faculty members and four graduate students, EDU-RU. The instrument used was the structured interview. The research findings indicated: 1) The degree of success, the importance of stage, and the modified Priority Needs Index (PNImodified) requirements for learning happiness among graduate students in the EDU-RU were at high levels respectively. The most crucial priority needs were satisfaction with a learning environment, followed by enthusiasm to learn, self-satisfaction, readiness to learn, and learning satisfaction, in that order: and 2) Approaches for learning happiness development among graduate students in the EDU-RU include happiness in classroom, cooperative among students, the use of technology, teaching pedagogies, and spirituality.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
แนวคิดและข้อเสนอแนะที่นำเสนอในบทความของวารสารการบริหารและความเป็นผู้นำทางการศึกษา มหาวิทยาลัยรามคำแหง เป็นแนวคิดที่มาจากผู้เขียน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบแต่เพียงผู้เดียว
ทั้งนี้ บรรณาธิการ กองบรรณาธิการ และคณะกรรมการหน่วยจัดทำวารสารฯ จะไม่ก้าวก่ายความมั่นคงในหลักการตามความคิดของผู้เขียน
ดังนั้น บรรณาธิการ กองบรรณาธิการ คณะกรรมการหน่วยจัดทำวารสาร และมหาวิทยาลัย จะไม่รับผิดชอบใด ๆ จากผลที่เกิดขึ้นจากการนำเสนอแนวคิด และข้อเสนอแนะของผู้แต่งที่เผยแพร่ในวารสารฯ
References
Bangun, Y. R., Pritasari, A., Widjaja, F. B., Wirawan, C., Wisesa, A. and Ginting, H. (2021). Role of Happiness: Mediatiing Digital Technology and Job Performance among Lecturers. Frontiers in Psychology, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychology/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.593155/full
Chanyanuvat, A., Han, W. and Xuexia, S. (2019). How to Help Students Learn with Happiness. Proceeding of RSU International Research Conference 2019, 808-816.
Clap, S. (2020). Peaceful and Happy Schools: How to Build Positive Learning Environments. Journal of Elementary Education, 12(4), 311-320.
Cohen, L., Manion, L. and Morrison, K. (2018). Research Methods in Education (8th ed.). London: Routledge.
Committee Announcement on Educational Standards: Criteria for Graduate-level Curriculum Standards B.E. 2022. (2023). Thai Government Gazette, 139, S212, 21-34. [In Thai]
Helliwell, J. F., Layard, R., Sachs, J. and Neve, J. E. D. (2020). World Happiness Report 2020. New York: Sustainable Development Solutions Network, Gallup World Poll.
Humaira, R. (2024). An Analysis of Teachers’ Pedagogical Competence in Using Technology for Learners. Thesis, Faculty of Education and Teacher Training, Ar-rainy State Islamic University.
Jamebozorg, Z., Jafarkhai, F. and Salimi, M. (2017). Designing a Happy Learning Environment in Schools and Investigating Its Relationship with Stress and Mental Health. Quarterly of Clinical Psychology Studies, 7(28), 121-133.
Joseph, D. (2019). Fostering a Happy Positive Learning Environment for Generalist Pre-service Teachers: Building Confidence that Promotes Wellbeing. British Journal of Music Education, 36(2), 183-196.
Ionescu-Felega, L., Ionescu, B. and Stoica, O. C. (2022). The Impact of Digitalization on Happiness: A European Perspective. Mathematics, https://doi.org/10.3390/math10152766
Laosum, T. (2023). Development of Indicators of Happiness in Learning of Thai Open University Students. Asian Association Open University Journal, 18(1), 61-77.
Mendo-Lazaro, S., Leon-del-Barco, B., Polo-del-Rio, M-I. and Lopez-Ramos, V. M. (2022). The Impact of Cooperative Learning on University Students' Academic Goals. Frontiers in Psychology, https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.787210
Noddings, N. (2003). Happiness and Education. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Paridinova, B., Sapartayeva, L., Tungatova, N., Tulepbergenovan, A. and Kassymbekova, M. (2023). Future Teachers' Spiritual Worldview Formation Factors. Education Research International, https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/9972903
Piatanom, P., Chongkhlaiklang, S., Thongkamhaeng, K., and Kotcharat, T. (2023). Happiness and Learning Experiences for Thai Children vs the Participation Management of Thailand Educational System. Shanlax International Journal of Education, 11(S1-Oct), 141-144. http://doi.org/10.34293/education.v11iS1-Oct.6675
Ramkhamhaeng University. (2022). Internal Quality Assessment Report of Graduate Programs, Faculty of Education, Academic Year 2022. Bangkok: Faculty of Education, Ramkhamhaeng University. [In Thai]
Srisa-ard, B. (2017). Preliminary Research. Bangkok: Suriyasasn. [In Thai]
Wongwanit, S. (2019). Research on Assessing Necessary Needs (4th ed). Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Press, Bangkok, Thailand. [In Thai]